MODBUS to a database: Write data to two different tablesDownload a Free Trial Version.It allows you to try all features!
Problem scenario: I have a database with two different tables. One table should store current data, and another table should save kilowatts per hour. Note: you may implement the same method and send data to multiple tables.
It is assumed that: You have configured the communication settings on the device:
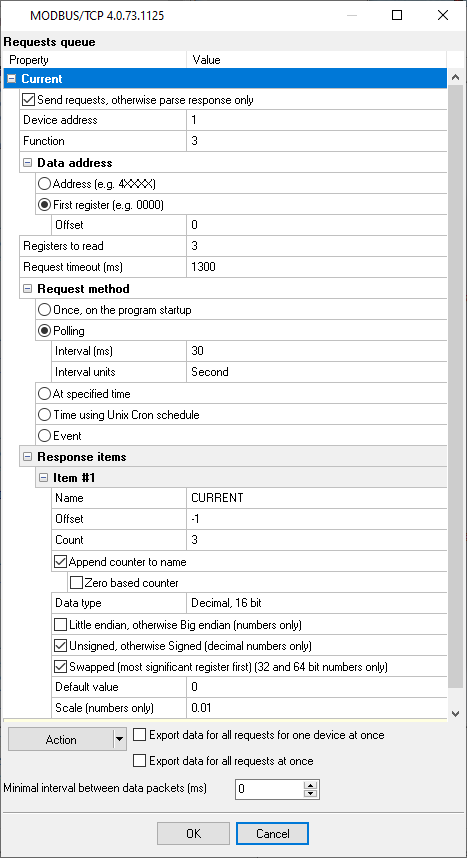
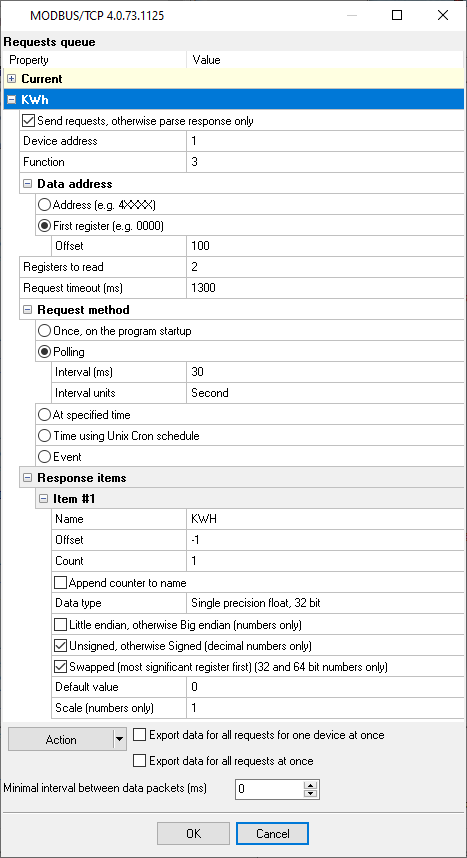
Solution: 1. You should create two MODBUS requests in a queue for the necessary data (fig. 1-3). One request should return data with current, and another request should return kilowatts. You may use different schedules for both requests. You may find more about how to configure the MODBUS queue here.
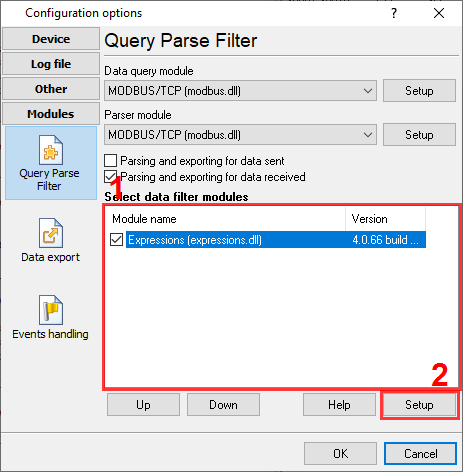
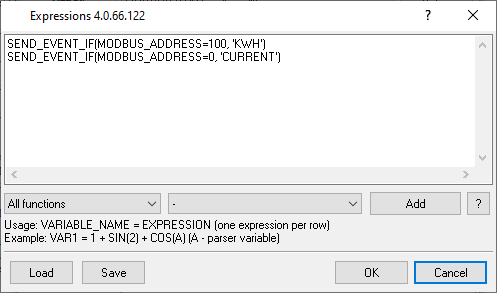
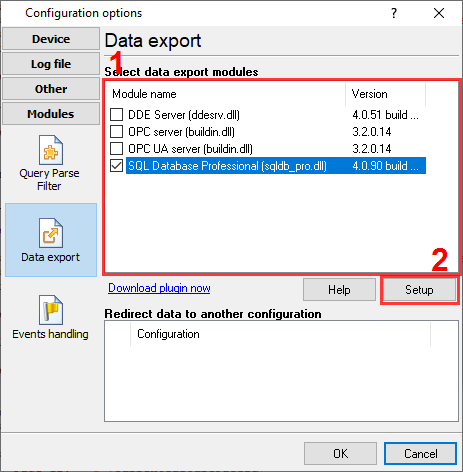
2. Create two tables in your database. We omit steps to create a user in your database and grant the "write" access rights to tables for your user. PHASE_1_CURENT - the column stores the current of the corresponding phase. KWH - the column stores kilowatts. DATE_TIME_STAMP - the time stamp when the program processes a response. 3. Enable and configure the Expressions plugin (fig. 4-5). The plugin will control an address of a MODBUS response and generate the corresponding event. The plugin will append all data from the MODBUS response to a generated event. Later, the SQL plugin will handle that event and execute a SQL statement.
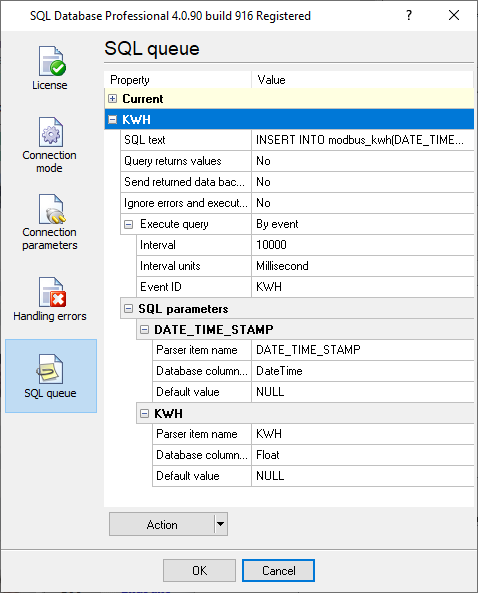
Here is the text copy of the expressions above: SEND_EVENT_IF(MODBUS_ADDRESS=100, 'KWH') SEND_EVENT_IF(MODBUS_ADDRESS=0, 'CURRENT') 4. Enable and configure the SQL Database Pro plugin (fig. 6-8). We omit connection settings here. You may find more info about it here. You should add two SQL statements for two generated events. Please pay your attention to the "Execute query" and "Event ID" fields in the settings.
Please check a data type when you bind the parser item name to a SQL parameter. It should match the data type of your column. Some data types can be converter automatically (e.g., integer → float or double).
5. Click "OK" to save the changes. 6. Check the status bar to ensure the data is being successfully processed (fig. 9).
Related articles: MODBUS to a database: Write data to two different tablesMODBUS RTU, MODBUS ASCII, MODBUS/TCP
BACNET/IPAdvanced TCP/IP Data Logger - Read more about:Serial port interface RS232 pinout and signals Cables and signals Data monitor cables |
|