Bacnet/IP Power Meter Data LoggingDownload a Free Trial Version.It allows you to try all features! Data logger plugins can be downloaded separately.
Problem scenario: My goal is to read values from the "Schneider Electric PowerLogic PM5300" power meter using the Bacnet/IP protocol. Requirements: The Bacnet/IP protocol implements data communication-based on an Ethernet network. For this reason, the module can be used in the logger with TCP/IP interfaces:
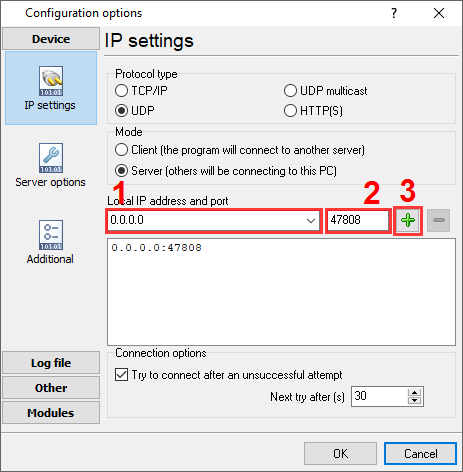
How to read data using MODBUS, you may read in another article. Background: This power meter can work with MODBUS and Bacnet. However, IMHO, Bacnet is easier to set up, because you do not need to know data types, offsets, combine several registers to one value, etc. It is assumed that: You have configured the communication settings (IP address, Subnet, Gateway, Bacnet Protocol) on the device. You must assign a static IP address for the device. Also, you need documentation for your device, that contains a description of all BACnet objects. In the Schneider Electric PM5300 series, we are interested in the "Analog Input objects" group with basic measurements (page # 41). Solution: 1. Configure the UDP server connection (fig. 1). The standard TCP port for Bacnet devices is 47808. The IP address should be "0.0.0.0". Then the program can receive data from all network interfaces on your computer. The IP address of your device you will specify later.
2. Enable the "Bacnet/IP" plugin (fig. 2).
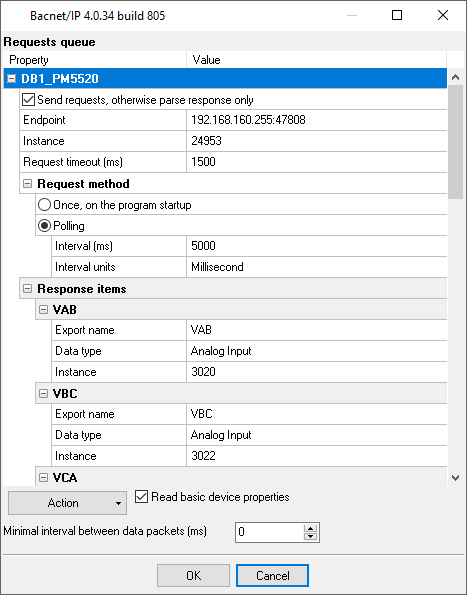
3. Configure the "Bacnet/IP" plugin by clicking the "Setup" button nearby (fig. 3).
4. Load the queue from the attached XML file by clicking the "Action - Load" button. This queue allows reading basic 10 values from the device. Also, you may load the full configuration using the "File - Restore configuration backup" menu item in the main window. 5. Adjust the polling interval as you want. 6. If you just want to write the parsed data to a file, then make the following changes:
7. If you need to write the parsed to Excel or a database, then you may continue using links below. All data export plugins use the same parser variables. You've defined the name of these variables in the "Export name" field (fig. 3). Related articles: Bacnet/IP Power Meter Data LoggingMODBUS RTU, MODBUS ASCII, MODBUS/TCP
BACNET/IPAdvanced TCP/IP Data Logger - Read more about:Serial port interface RS232 pinout and signals Cables and signals Data monitor cables |
|